Epithelial tissue is a crucial component of our bodies, playing a vital role in protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration. It serves as a lining for various organs, ducts, and cavities, forming a barrier against potentially harmful substances. Understanding the main characteristics of epithelial tissue is fundamental in grasping its significance. In this blog post, we will explore the structure and function of epithelial tissue, its different types, and its appearance under a microscope. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of epithelial tissue and uncover its secrets!
Keep reading to explore the different types of epithelial tissue, examine its distinct characteristics, and discover where it can be found within our amazing human bodies.
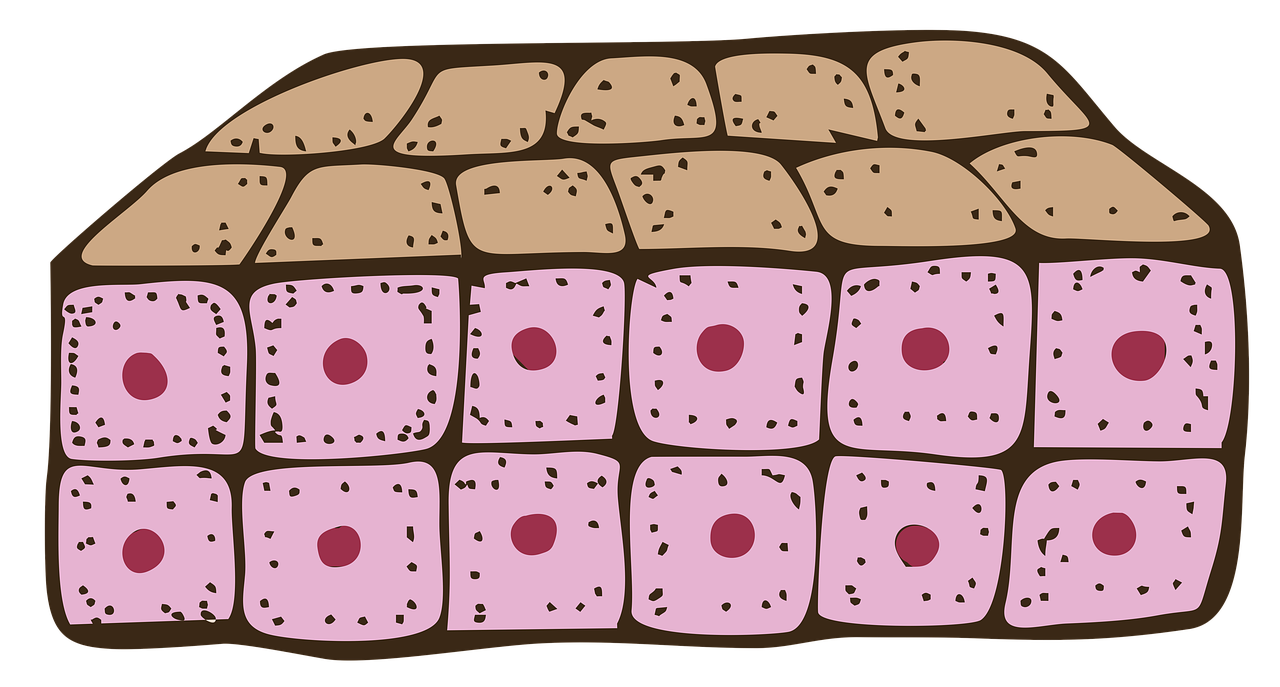
What Are the Main Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissue is like the superstar lining your body, protecting and secreting like a boss. From the smooth surface of your skin to the intricate lining of your organs, epithelial tissue has got it all covered. Let’s dive into the main characteristics that make this tissue so special.
An Airtight Barrier: Epithelial Tissue Keeps It Together!
Epithelial tissue acts like the bouncer of your body, regulating the movement of precious substances in and out. With its tight cell connections, it forms a barrier that keeps your inner world separated from the chaos of the outside. No sneaky intruders can get past this badass defense!
Beautiful Shapes and Sizes: Squamous, Cuboidal, and Columnar, Oh My!
Epithelial cells come in all shapes and sizes, adding a touch of variety to their function. Some are squamous, flat like pancakes, perfect for slippery surfaces like blood vessels. Others are cuboidal, box-like cells that contribute to secretory glands. And we can’t forget the columnar cells, elongated pillars suited for absorption duties in the intestines. These shape-shifters definitely know how to work it!
Super Specializations: Meet the Glands and Their Secret Operations!
Ever wondered where all those secretions come from? Well, it’s the epithelial tissue that’s got it covered! This tissue boasts an array of glands, from salivary glands that start the digestion party to sweat glands that keep you feeling cool. Whether it’s mucus, tears, or hormones, epithelial tissue has the top-secret clearance to handle it all. Talk about multi-talented!
Nerve Tissue: Epithelial Tissue’s Distant Cousin with a Secret Friendship
Although not a characteristic exclusive to epithelial tissue, it shares a close bond with nerve tissue. These unlikely friends often team up, with the nerve tissue providing instructions while the epithelial tissue executes like a boss. Together, they form some killer combos, like the taste buds on your tongue or the touch receptors on your skin. It’s a beautiful partnership that keeps you feeling alive and aware!
Adaptable and Regenerative: Epithelial Tissue Bounces Back!
No matter how tough the battle, epithelial tissue knows how to bounce back from the brink of destruction. It has the remarkable ability to regenerate and repair itself, keeping your body in tip-top shape. Whether it’s a small scrape or a burn, these superstar cells hustle their way back to normalcy. It’s like having a team of dedicated repair workers on standby!
Epithelial tissue may be hidden from sight, but it’s a powerhouse of protection, secretion, and regeneration. From forming barriers to producing secretions, this tissue is the unsung hero of your body. So, next time you feel a sense of gratitude for that smooth skin or functioning organs, remember to give a shout-out to the amazing epithelial tissue. You rock, little cells!
FAQ: What are the main characteristics of epithelial tissue?
What are the 3 main types of connective tissue
Connective tissue comes in various types, but the three main ones are:
-
Fibrous connective tissue: This type of connective tissue is known for its strength and ability to withstand tension. It can be found in tendons and ligaments, which are responsible for connecting muscles and bones.
-
Adipose tissue: Also known as fat tissue, this type of connective tissue serves as the body’s energy storage and insulation. So, next time you blame your love handles, just remember they’re keeping you warm!
-
Cartilage tissue: Cartilage tissue is found in areas like your ears and nose. It provides structure and support while still allowing for some flexibility. So, you can thank your cartilage for that dazzling nose wiggle you’re so proud of!
What are the 12 tissue types
The human body is a masterpiece composed of 12 different tissue types. These include:
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Nervous tissue
- Blood tissue
- Bone tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Cartilage tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Lymphoid tissue
- Hematopoietic tissue
- Glandular tissue
So, as you can see, we’ve got quite the variety pack going on in our bodies!
What are 3 general characteristics of connective tissue
Connective tissue is like the glue that holds us together. Here are three general characteristics that make it oh-so-special:
-
Diversity: Connective tissue is incredibly diverse, with various types serving different functions throughout the body. It’s like a secret agents’ squad, each member having their own unique skills.
-
Abundance: It’s everywhere! Connective tissue can be found in bones, blood vessels, tendons, and even your eyeballs. It’s the supporting cast that keeps our bodies intact and functioning.
-
Extracellular matrix: Connective tissue is all about teamwork. It consists of cells suspended in an extracellular matrix that provides structural support and nourishment. Think of it as the ultimate team-building exercise for cells!
What are 5 characteristics of connective tissue
Connective tissue has got some swagger! Here are five characteristics that set it apart from the rest:
-
Cellularity: Connective tissue may be diverse, but one thing it’s not is lonely. It’s packed with cells that perform various functions, like producing collagen or gobbling up bacteria. Talk about a busy social scene!
-
Vascularity: Some connective tissues, like adipose tissue, are well-vascularized, meaning they have a rich blood supply. Others, like tendons, have a more limited blood flow. It’s like a real estate market for blood vessels!
-
Extracellular matrix: We mentioned it before, but it’s worth highlighting again. Connective tissues are surrounded by an extracellular matrix composed of fibers and ground substance. It’s like a fancy cocktail party, with fibers mingling in a sea of goop!
-
Strength and support: Connective tissue is all about providing structure and support to the body. It’s like a supportive friend who always has your back, literally!
-
Specialized cells: Connective tissues have some pretty cool cells with fancy names, like fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and osteocytes. They do all the heavy lifting and keep things running smoothly. It’s like having a team of superheroes guarding your body!
What are the 6 main types of connective tissue
Just as there are different flavors of ice cream, connective tissue comes in six main types:
-
Loose connective tissue: This type of connective tissue is like the fluffy clouds in the sky, providing cushioning and support for organs.
-
Dense connective tissue: If loose connective tissue is a fluffy cloud, dense connective tissue is a brick wall. It’s strong and durable, found in tendons and ligaments.
-
Cartilage: Cartilage is like the cushioning in a fancy pair of shoes. It’s flexible and acts as a shock absorber in our joints.
-
Bone tissue: Bones are our body’s architecture. They give us structure, protect our organs, and store those essential minerals.
-
Adipose tissue: Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is that friendly holder of energy and insulation. Who needs a Snuggie when you’ve got adipose tissue?
-
Blood tissue: Ah, the life-sustaining liquid. Blood tissue is responsible for carrying oxygen, nutrients, and those cool immune cells that keep us healthy. It’s like the neighborhood watch of our bodies!
What are the general structural characteristics of connective tissues? What are the functions of connective tissues? And how are their functions reflected in their structures
Connective tissues come in different shapes and sizes, but they share some key structural characteristics and functions:
-
Fibers: Connective tissues feature various fibers, including collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers. These fibers give connective tissues their strength, flexibility, and stretchiness.
-
Ground substance: Connective tissues have a ground substance, a gel-like substance that fills the spaces between cells and fibers. It provides support, lubrication, and a transport highway for nutrients and wastes.
-
Cells: Connective tissues are packed with a diversity of cells, each with its specific function. We’ve got fibroblasts, osteocytes, chondrocytes, and many more! It’s like a bustling city, with each resident playing their part.
Now, let’s talk functions:
-
Support and protection: Connective tissues provide structural support and protection to our organs, bones, and joints. They keep everything in place and absorb the shocks of daily life.
-
Connection: Connective tissues, like tendons and ligaments, connect muscles to bones and bones to bones. They’re the bridges that allow our body parts to communicate and coordinate.
-
Transportation: Blood, a connective tissue, transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells throughout the body. It’s like a bustling highway, keeping everything running smoothly.
-
Energy storage: Adipose tissue stores energy in the form of fat. So, when you skip a meal, your adipose tissue swoops in and saves the day!
-
Immune response: Connective tissues play a crucial role in our immune response. They house immune cells that fend off pesky bacteria, viruses, and other intruders. It’s like having a security team on high alert!
What are the 10 types of connective tissue
Connective tissue is a diverse cast of characters. Here are the ten types that make up our body’s connective tissue ensemble:
- Loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone tissue
- Blood tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Lymphoid tissue
- Hematopoietic tissue
- Glandular tissue
It’s like a blockbuster movie with an all-star cast, each type playing its unique role in keeping us healthy and happy!
What are the 9 types of connective tissue
Connective tissue is ready to impress with nine different types:
- Loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone tissue
- Blood tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Lymphoid tissue
- Hematopoietic tissue
With such variety, it’s like trying to choose your favorite Netflix series. Good luck picking just one!
Is epithelial tissue the same as skin
Ah, the skin, our body’s protective coat! While epithelial tissue does play a significant role in our skin, it’s essential to remember that epithelial tissue is not limited to just the skin. Epithelial tissue covers our organs, lines our blood vessels, and even makes up the lining of our digestive tract. So, epithelial tissue is like a versatile superhero costume, capable of protecting us both inside and out!
What are the main characteristics of epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue deserves a standing ovation for its main characteristics:
-
Cellularity: Epithelial tissue is made up of closely packed cells, like a row of well-behaved students. They form a barrier that protects underlying tissues and organs.
-
Polarity: Epithelial cells have a distinct top (apical) and bottom (basal) side. It’s like a well-coordinated dance routine, ensuring each cell knows its place.
-
Attachment: Epithelial cells are excellent huggers! They’re tightly connected to each other through special cell-to-cell junctions, forming a robust and seamless barrier.
-
Avascular: Epithelial tissue doesn’t need a bloodstream to get things done. It receives nourishment through diffusion or absorption from underlying tissues. Talk about being independent!
-
Regeneration: Epithelial tissue is a master of rebirth! It has a high regenerative capacity, allowing it to repair and renew itself quickly. It’s like a superhero with speedy healing powers!
What is the structure and function of epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue is the body’s ultimate multitasker. Its structure and function can’t be overlooked:
Structure: Epithelial tissue has tightly packed cells arranged in continuous sheets or layers. These sheets can be simple, with one layer, or stratified, with multiple layers. We’ve got squamous cells, cuboidal cells, columnar cells, all with their unique shapes and sizes.
Function: Epithelial tissue wears many hats. It acts as a protective barrier, keeping out harmful substances and pathogens. It also allows for selective absorption and secretion, ensuring our bodies absorb valuable nutrients and get rid of waste efficiently. Add in its sensory functions and involvement in gas exchange, and you’ve got a true MVP!
What are the 8 types of connective tissue
Connective tissue is like an exciting world with eight different types:
- Loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone tissue
- Blood tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Lymphoid tissue
Our bodies are a connective tissue extravaganza, with each type playing a vital role in keeping the show running smoothly!
What does epithelial tissue look like
Epithelial tissue comes in all shapes and sizes, like a fashion runway for cells. We’ve got squamous cells, which are thin and flat like fried potato chips. Then there are cuboidal cells, which resemble cozy little cubes. Finally, we have columnar cells, long and slender like elegant pillars. It’s like a cell fashion show, where diversity and unique styles are celebrated!
What are 4 characteristics of epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue rocks four standout characteristics:
-
Selective permeability: Epithelial tissue is like a bouncer, carefully selecting who gets to enter our body and who gets the boot. It allows for selective transport of substances, making sure only the worthy ones pass through.
-
Protection: Epithelial tissue is our body’s personal bodyguard. It forms protective barriers to shield our delicate tissues from harm, just like a bouncer protecting a VIP party.
-
Secretion: Epithelial cells love to surprise us by secreting specialized substances like hormones and enzymes. It’s like little gift packages of biochemical wonders!
-
Absorption: Epithelial tissue gets a gold star for absorption. It’s responsible for absorbing nutrients, water, and other good stuff from our digestive tract, ensuring our bodies get the most out of our meals.
Epithelial tissue: the hardworking multitasker we can’t live without!
What are the 6 characteristics of epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue is a powerhouse when it comes to characteristics, sporting six noteworthy ones:
-
Cellularity: Epithelial tissue is packed with cells, like a crowded elevator during rush hour. These cells work together as a team, forming tight junctions to create a robust barrier.
-
Polarity: Epithelial cells have a defined top and bottom, like the Harry Styles haircut of tissues. This polarity helps them carry out their specific functions effectively.
-
Specialized structures: Epithelial tissue isn’t just cells holding hands; it has some cool specialized structures. We’re talking microvilli for increased surface area and cilia for gentle cell wafting. It’s like having an army of tiny superheroes with superpowers!
-
Avascularity: Epithelial tissue may not have blood vessels of its own, but it knows how to play the game. It gets nutrients through diffusion from neighboring tissues, like a ninja hijacking resources unseen.
-
Regeneration: Epithelial tissue is the master of comebacks. It can regenerate quickly, healing wounds and replacing damaged cells faster than you can say “cellular superhero.”
-
Attachment: Epithelial cells stick together like BFFs. They form tight junctions, adherens junctions, and desmosomes. It’s like a friendly community, where cells are always there to lend an adhesive hand.
What body part contains epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue is like the body’s jack-of-all-trades, found in various parts of the body. It covers our organs, lines our blood vessels, wraps around our muscles, and even makes up the outer layer of our skin. It’s like the versatile ingenuity that ensures our body works like a well-oiled machine!
